Solving for unemployment: A study on matching skill demand and supply

Client: Rockefeller Foundation
Challenge
Addressing the gap between youth skilling and livelihood generating interventions’ in India
Outcome
An evidence based 3 pillar framework (or model) for developing effective public and private skilling interventions in India
India’s current demography provides for a great opportunity for the country to leapfrog both economic growth and development milestones. However, for the country to use its youth productively, there is a requirement for skilling interventions that appeal to the youth. Currently, most interventions see sub-optimal participation because of; (i) misalignment of interest and aspirations of youth with the courses in the institutes; (ii) low recognition of the certifications and diplomas offered at these institutes and; (iii) low economic gains from these skill trainings. Consequently, India is currently witnessing a situation where youth are seeking suitable openings in the job market for their skills, while companies and enterprises concurrently have unfilled vacancies.
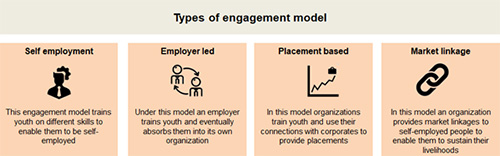
With the objective of strengthening youth skilling programs in India and scaling interventions that are effective, Rockefeller Foundation engaged with Intellecap to examine the landscape of interventions, both government-run and private sector, that aimed at youth skilling and livelihood generation in India. The study analyzed more than 80 organizations in this space, and highlighted some interesting insights and constraints that hinder youth skilling and employability in India. It found that programs and organizations in the space currently adopt one of four engagement models: the self-employment model, the employer led model, the placement-based model and the market linkage model. Each of these models has associated strengths and weaknesses, and has played a critical role in reducing youth unemployment in India.
In order to address that cause unemployment and underemployment amongst youth, Intellecap found an underlying need to develop well-designed interventions that are regularly monitored and evaluated for best practices. These interventions need to focus on three pillars: youth aspirations, industry requirements, and standardization across stages of the skill development value chain for rapid scalability. In addition, Intellecap notices that partnerships between private and government stakeholders in this space and cohesive efforts to develop evidence-backed interventions for skill development can help in attaining security, stability and opportunities for all, thus allowing India to leverage its demographic dividend.